一级标题
一级标题
Avoid your inquiry is delay response, please enter your WhatsApp/Skype along with the message, so we can contact you at the very first time.
We will reply you within 24 hours. If for urgent case, please add WhatsApp/WeChat:
Warning: Undefined variable $public in /www/wwwroot/lvfertilizer.com/wp-content/themes/hyhadmin/header.php on line 350
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /www/wwwroot/lvfertilizer.com/wp-content/themes/hyhadmin/header.php on line 350
,. Or call
Warning: Undefined variable $public in /www/wwwroot/lvfertilizer.com/wp-content/themes/hyhadmin/header.php on line 350
Warning: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /www/wwwroot/lvfertilizer.com/wp-content/themes/hyhadmin/header.php on line 350
directly.
Crops slow down, leaves go pale, and profits shrink. Many growers feel stuck and frustrated by weak soil and low yields. I was there too, until I learned the real meaning behind NPK.
NPK means nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These are the three key plant nutrients. NPK fertilizer blends deliver all three at once, making feeding easier and more effective for every crop.
If you want bigger harvests and healthier fields, it pays to know why these three letters matter. Let me walk you through the science, the benefits, and how I help clients worldwide use the right NPK for every farm.
Plants need the right fuel to reach their full size and flavor. Many growers use only what’s cheap or nearby, but that can leave hidden gaps and missed profits. I have seen fields transform after using a proper NPK blend.
NPK is best for complete plant development—fast green growth, strong roots, and big, healthy fruits. Each part of NPK does a specific job that cannot be replaced.
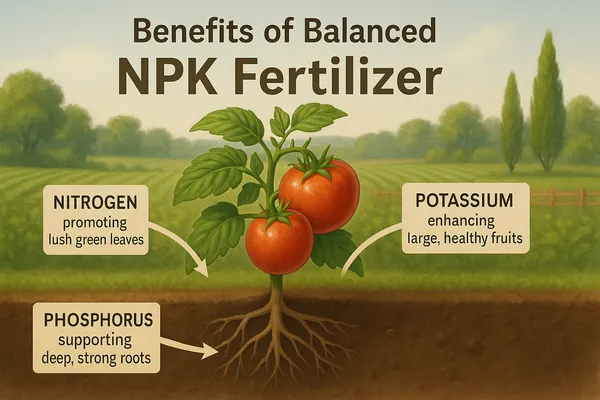
Benefits of balanced NPK fertilizer
| Nutrient | Role in Plants | Visible Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N) | Makes leaves green, powers growth | Taller stems, lush leaves |
| Phosphorus § | Builds roots, flowers, and fruit | More blooms, bigger fruit |
| Potassium (K) | Strengthens cells, guards against disease | Firm fruit, drought-tolerant |
Tip: Always test your soil first. Even a good fertilizer needs the right starting point.
When I used single-nutrient products—like just urea or DAP—my crops often suffered. Lettuce turned yellow. Tomatoes dropped blossoms. Balanced NPK blends solved these problems and made results predictable. In field trials run with my clients, NPK blends increased yields by 10–18% compared to old methods.
| Crop Stage | Recommended NPK Ratio | Reason for This Choice |
|---|---|---|
| Seedling | 20-20-20 | Uniform boost to leaves and roots |
| Early Growth | 30-10-10 | High N for rapid leaf formation |
| Flowering/Fruiting | 10-30-20 | More P and K for strong blooms/fruit |
| Maturity | 10-10-30 | Potassium to strengthen and finish crop |
In my own fields, I’ve seen rice respond to a starter blend (12-24-12) and then finish strong with a high-potassium topdress (13-5-40+TE). Matching the right NPK to the crop stage is a major key to consistent yields.
“Since we switched to a customized NPK blend, our output per hectare rose by 14%, and fertilizer use actually dropped.”
— Agribusiness Client, Brazil
When I started using 20-20-20 fertilizer, I was amazed at how quickly my vegetables perked up. Growth was fast, and even my weaker seedlings bounced back.
20-20-20 fertilizer is an all-purpose, water-soluble NPK blend for early growth, stressed crops, and uncertain soils. It delivers a perfect balance of major nutrients in every dose.
| Application Type | Benefit of 20-20-20 NPK | Example Use |
|---|---|---|
| Seedlings | Jump-starts roots and shoots | Greenhouse trays, plug plants |
| Drip irrigation | Rapid uptake for vegetables and fruit | Tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers |
| Foliar feeding | Quick fix for nutrient deficiencies | Leafy greens, ornamentals |
| Lawns and turf | Restores color and thickness | Sod farms, golf courses |
| Hydroponics | Fully soluble, feeds all plant organs | Lettuce, herbs, strawberries |
20-20-20 is a favorite because it dissolves easily and flows through irrigation systems or sprayers. I have seen even tired fields bounce back after just one or two applications. A large melon farm in Shandong, after a season of water-soluble 20-20-20, reported a 13% jump in marketable yield and better fruit color.
My own 20-20-20 formulas often include iron, zinc, and manganese. These trace elements correct hidden deficiencies, especially in greenhouse and sandy soils.
Clients often ask me if a single NPK blend will work for all crops. I always say, “Yes, but only if you adjust the ratio for the plant’s true needs.”
All plants need nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, but each plant and growth stage requires a different balance. Tailored NPK blends give the best results and protect sensitive crops.
| Crop Type | Common NPK Ratio | Why This Ratio? |
|---|---|---|
| Leafy greens | 25-10-10 or 30-10-10 | Pushes fast leaf growth |
| Root vegetables | 10-20-20 or 12-24-12 | Supports deep roots and storage |
| Fruit crops | 15-5-30 or 15-15-30 | Balances sugar, firmness, shelf life |
| Flowers/ornamentals | 10-30-20 or 15-30-15 | Stimulates blooms and color |
In my experience, too much nitrogen late in the season weakens fruit and storage. Extra phosphorus in some soils can get “locked up” and wasted. That’s why I always recommend a soil test first, then fine-tuning NPK. My lab can help analyze samples and craft a formula for your region.
A citrus grower in Egypt used a standard 20-10-10 for years but suffered leaf drop. After switching to a region-specific NPK with more potassium and added iron, yield increased and fruit quality stabilized—proving the power of tailored nutrition.
Key Point: NPK fits every plant, but success depends on choosing the right blend and application timing.
Many farmers I meet still rely on urea for nitrogen because it’s cheap and familiar. I did too, but I learned the hard way that single-nutrient feeding can hurt both plants and profit in the long run.
NPK is better than urea because it supplies all major nutrients, keeps soils healthier, and increases yields more reliably. Urea is only nitrogen—without P and K, plants are incomplete.
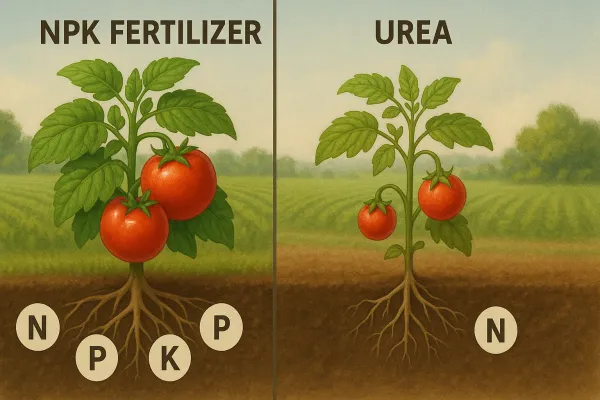
NPK fertilizer vs urea comparison
| Feature | NPK Fertilizer | Urea |
|---|---|---|
| Nutrients Provided | Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium (+TE) | Only Nitrogen (46%) |
| Effect on Yield | Balanced, higher, stable | Short-term lush growth, poor fruit |
| Soil Health | Maintains pH, structure, microbe activity | Acidifies soil, harms microbes |
| Loss Risk | Lower—less volatilization/leaching | High ammonia loss, quick leaching |
| Environmental Impact | Controlled, less runoff | Greater pollution risk |
| Cost per Season (all nutrients) | Lower in long term (less supplementing) | Higher if adding P/K later |
Tip: Urea may seem cheaper per bag, but adding P and K later often raises total cost—and doesn’t correct early-season nutrient gaps.
In 2023, I set up two maize plots in Shandong. One used standard urea (300kg/ha), the other a balanced NPK 20-10-20 (300kg/ha total). The NPK field yielded 12.4 tons/ha, with stronger stalks and fewer disease problems. The urea-only field was lush early but yielded just 10.7 tons/ha, and several plants lodged before harvest.
“After switching from straight urea to water-soluble NPK, we saw not just higher yields, but better grain weight and less fertilizer burn,” says Ms. Li, a farm manager in Jiangsu.
Q: What does the ratio in NPK fertilizer mean?
A: It shows the percentage by weight of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P₂O₅), and potassium (K₂O). For example, NPK 15-15-30 means 15% N, 15% P₂O₅, and 30% K₂O.
Q: How often should I use NPK fertilizer?
A: This depends on crop type, growth stage, soil test, and fertilizer formulation. For most vegetables and field crops, 2–4 applications per season works best.
Q: Can I order custom NPK blends for my local soil?
A: Yes, I offer region-specific formulas. My technical team analyzes soil and climate data to design the right blend for your needs.
Q: Is NPK fertilizer safe for the environment?
A: Balanced NPK use reduces runoff and pollution compared to overuse of single nutrients. My factory is ISO 9001 certified, meeting strict safety and quality standards.
Case Study
A strawberry grower in California switched from generic granular fertilizer to my custom water-soluble NPK 19-19-19+TE. In the first season, berry size and sweetness both improved. Soil pH remained stable, and input costs fell by 9%. “We used to have uneven ripening. Now every box is more uniform and marketable,” the grower shared.
NPK means full-spectrum nutrition for every plant. The right blend, applied at the right time, leads to bigger yields, healthier soil, and stronger profits.